What is textile? The Classification of Textiles, which textile test equipment?
Section 1: What is textile? The Classification of Textiles
To start to get the answer of what is textile? First, let’s understand textiles, and the classification of textiles, this section will cover the most comprehensive aspects of how to classify textiles.
In lay man’s terms, textiles can be referred to as the three main series of woven, knitted fabrics, and non-woven.
But extensively, textiles involve, spinning weaving, and finished products, such as:
- Yarn, natural silk, elastic silk, metallic silk, synthetic long and synthetic short silk, rayon, and other textile raw materials.
- Woven and non-woven fabrics, plastic fabrics, knitted fabrics, natural fur fabrics, and industrial fabrics. Industrial fabrics are the textiles used in the industrial field like canopy cloth, sieve, filter cloth, and the like.
- Bags, blankets, household textiles, gloves, socks, decorative clothing products, and other fabricated products.
- Other types of textiles include; clothes for toys, belts, rope, sable, sewing, and embroidery thread.
a.) Methods in which textiles are processed
- Knitted fabric textile: the surface of a knitted fabric feels soft, comfortable on the body, and rich in elasticity.
- Woven fabric textile: this fabric has no elasticity except for the type of fabric that has an elastic fiber. It has a stable structure with a flat surface. Very solid, easy to wear, and has a stiff and loose appearance.
- Non-woven fabric textile: this involves using polymer slices, filaments, or short fibers through different kinds of the fiber network. This further creates a fusion of methods and technology and the end products are soft flat and breathable new fiber products.
Let’s have an extensive look at the three methods of processing textiles, this is for those who want to dive deeper into the topic of what is textile.
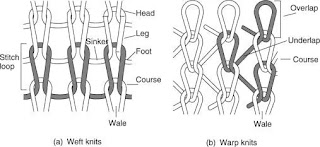
I.) Knitted Fabrics: the yarn is woven into a circle and the fabric is formed and divided into two, weft knit and warp knit.
- Weft Knit: In a weft knitted fabric, the weft is put into the working needle of the knitting machine. This is to enable the yarn to bend into a circle and each other through the sleeve. The yarn moves horizontally from one side of the machine to another in a circular motion, and a new knitting loop can be formed with the needle’s movement.
As the yarns go horizontally, the fabric is formed by knitting a horizontal row of loops in the same pattern and direction with the bottom and top rows connected to each other. All of the loops are knitted from a single yarn. Weft knitting can either be done on a circular knitting machine or a flat one. Weft knitted fabrics are used in making sweaters, socks, etc.
Fabrics that have been weft knitted hold the largest proportion when it comes to knitted products.
- Warp Knit: in a warp knitted fabric, a group of yarns is arranged in parallel and put into the working needles of the knitting machine all at the same time loop. Warp knitting entails a longitudinal movement of a set of warp yarns up the warp and needle movement as well to produce knitted warps. Warp knitted fabrics, and the warp knitting machines used in producing them have a significant difference from weft knitted fabrics and the weft knitting machines that make them. Just like the warp in woven fabrics, the yarns are warp knitted in warp knitted fabrics. These are supplied by a warp beam that is covered with an enormous amount of parallel yarns in rows. Just like what you will see in the warp beam in woven fabrics. In a warp woven fabric, all the yarns are warp directed. In a single horizontal row, a vertical coil is made. This now moves in a diagonal pattern to a different vertical row, thus creating another coil in the next horizontal row. As the yarn moves in a zigzag manner from side to side covering the length of the fabric, each loop is in a horizontal row and is knitted with a different yarn.



评论
发表评论